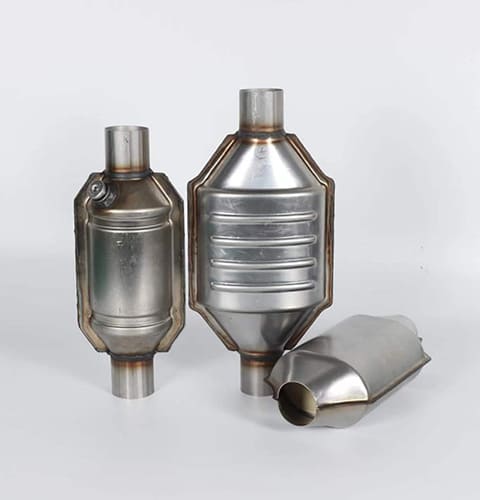
Have you ever wondered how modern gasoline vehicles manage to keep their emissions low? Or perhaps, you’ve heard about the latest environmental regulations and wondered how car manufacturers are adapting? Enter the Gasoline Particulate Filter (GPF), a relatively new player in the world of vehicle emission controls. But what exactly is a GPF, and why is it becoming increasingly important in today’s automotive landscape?
A Gasoline Particulate Filter, commonly referred to as a GPF, is a device installed in the exhaust system of modern gasoline-powered vehicles. Its primary function is to capture and store particulate matter (PM) emissions, which are tiny particles of soot and metal oxides. These particles, if released into the atmosphere, can have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. The introduction of GPFs has been largely driven by stricter emission standards, such as the Euro 6 regulation in Europe, which aim to reduce the environmental impact of vehicles.
Understanding the role and importance of GPFs is crucial, especially as the automotive industry shifts towards cleaner and more efficient technologies. As consumers, being informed about these developments not only helps us make better vehicle choices but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the technological advancements that are shaping a greener future.
How Does a Gasoline Particulate Filter Work?
How exactly does a GPF capture and remove particulate matter from exhaust gases? And what makes it different from other emission control devices like catalytic converters or diesel particulate filters (DPFs)?
The core function of a GPF is to physically trap particulate matter as exhaust gases pass through it. These filters are made from materials like cordierite or silicon carbide, which provide a porous structure that captures the particles. Once trapped, the particles are burned off through a process called regeneration. This process involves heating the filter to a high temperature, which burns off the particulates, turning them into less harmful gases.
What sets GPFs apart from DPFs, commonly used in diesel engines, is their ability to operate effectively at the lower exhaust temperatures typical of gasoline engines. This capability is crucial, as gasoline engines generally produce fewer particulates than diesel engines, but the particles they do emit are smaller and more difficult to capture.
Why Are GPFs Increasingly Important?
Why is there a growing emphasis on incorporating GPFs in modern gasoline vehicles? And how do they contribute to environmental sustainability?
GPFs have become increasingly important due to stricter emission standards worldwide. For instance, the Euro 6 standards, which set limits on particulate matter emissions, have made GPFs essential in many new gasoline vehicles. These filters are particularly important in direct injection gasoline engines, which tend to produce more particulate matter compared to traditional port injection engines.
The role of GPFs extends beyond just complying with regulations. They are a key component in the broader effort to improve air quality and public health. By reducing particulate matter emissions, GPFs contribute to cleaner air, which is crucial in urban areas where air quality is often poor. Additionally, as we move towards more sustainable mobility solutions, technologies like GPFs play a vital role in bridging the gap between traditional internal combustion engines and cleaner alternatives.

Conclusion
Gasoline Particulate Filters represent a significant step forward in reducing vehicular emissions and improving air quality. As regulations continue to evolve and the automotive industry progresses towards cleaner technologies, understanding and appreciating these innovations becomes increasingly important. Whether you’re a car enthusiast, an environmental advocate, or just someone concerned about air quality, the role of GPFs in modern vehicles is an exciting and crucial development in our journey towards a more sustainable future.


